Introduction to Billing-as-a-Service (BaaS)
Summary
Insurers send out a lot of bills. It's an expensive process — not just in terms of the physical costs of printing, paper, and postage: credit card fees add up, and human beings are needed to answer questions, manage accounting, and oversee reconciliation. Some think of it as the most "back-office" of the back-office processes — one which adds little to no strategic value. After all, every insurer can collect money. The basic ability to do so is not a differentiator. But for many customers, the bill is the most frequent contact they have with their insurer. And for many insurers, legacy billing systems simply don't meet the challenge of high service expectations from today's consumers, business customers, and distribution partners.
Consumers today expect much more flexibility in how their bill is handled and expect transparency in their payment history. They expect to be able to change bill types easily (e.g., go from agency pay to direct pay at midterm). They may need to change from payroll deduction to direct pay because of a disability situation. And they may have split billing, where one auto on the policy is billed to a student while at university and the other are billed to the parents.
Insurers certainly have the option of selecting a modern billing system that has robust capabilities to handle these kinds of situations. But an increasing number of insurers are questioning the overall costs of handling billing. Rather than replacing their billing system in order to provide new capabilities, they're deciding to outsource the whole process.
We've seen increased interest in outsourcing this process due to the pandemic. As insurers began to enact work from home, they found some employees still had to come to the office in order to collect and manage the billing process.
Billing-as-a-Service (BaaS) is an alternative that insurers can use to manage this essential function without putting their own employees at risk — often resulting in reduced costs and improved services.
This primer explains what BaaS is and how it typically works. It describes the features to look for when selecting a provider and provides a profile of one of the providers that are active in the property casualty insurance marketplace.
Billing as a Service (BaaS) is essentially the outsourcing of all aspects of managing the billing process. It provides receivables management services (as opposed to outbound claims payments).
How Does Insurance Billing Work Today?
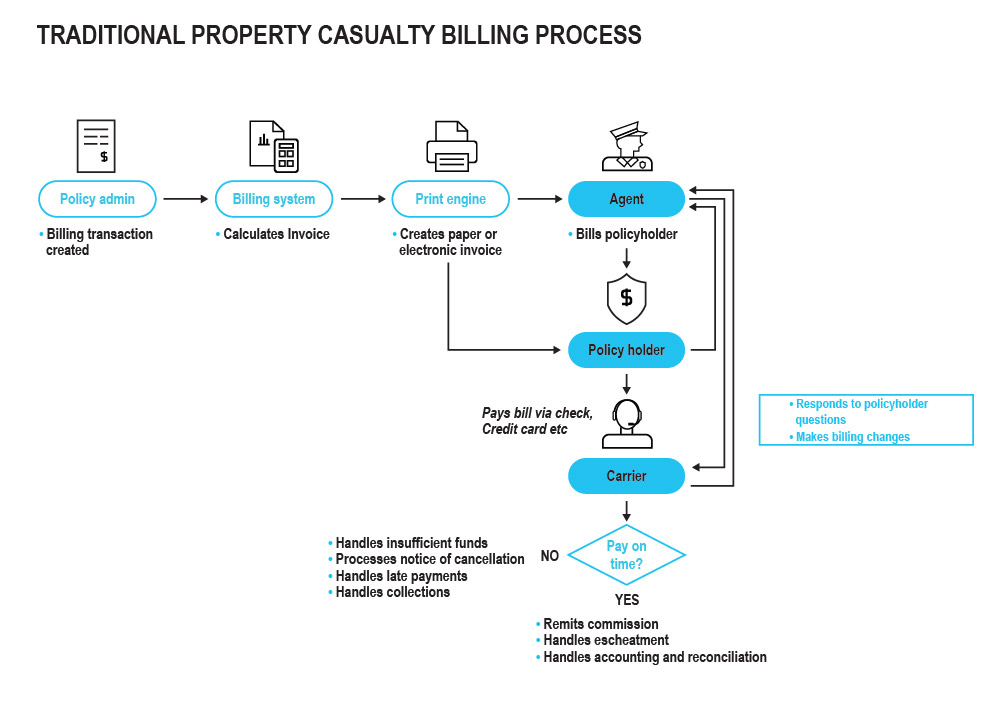
The typical billing process inside an insurer starts with the calculation of a premium transaction in the policy admin system. For property & casualty insurers, that calculation is sent to a billing system, which manages the definition of the payment plans and determines how much the actual bill will be. It keeps rules such as whether to spread the amount due over future payments. Once the payment due is calculated, the data about the bill is typically sent to a print stream to create a paper bill or an electronic bill. For life insurers, those steps are typically handled in the policy administration system.
Bills may be sent directly to the policyholder, to an agent, or to an employer. While agent bill isn’t as common today as in the past, there are still a number of insurers, primarily property & casualty, who do use agent bill either account current or statement bill. The billing system also calculates the commission due to the agent on the transaction and is occasionally used to create the commission statement and track payments to the agent.
The insurer also has a set of processes to manage the collection of money. They may collect via credit card, ACH, or a lockbox. The billing system will track grace periods, late payments, and insufficient fund transactions. It uses business rules to determine whether a policy needs to be canceled for non-payment or if it needs to go into collections. From a customer service standpoint, the insurer will answer questions from the insured about the payment and may, from time to time, change features such as billing due dates, payment plans, or payment methods.
Figure 1: Traditional Property Casualty Billing Process
How Does Billing as a Service (BaaS) Work?
The most typical process is similar to that described in the process above. But with BaaS, the payment due is sent to the BaaS provider instead of to an output file (print or email). The BaaS provider takes over all functions from there. They send the bill to the customer using the mechanism the customer chooses. They collect the funds and remit them back to the insurer. They provide customer service support for those questions that are most common and transfer them to the insurer when they are more complex.
Life insurers and some property casualty insurers send the data directly from the policy admin system, bypassing a billing system altogether. In this instance, the BaaS provider will manage the definition of the payment plans, calculate the amount of payment that is due, apply fees, and provide other functionality inherent in a traditional billing system.
Figure 2: Property Casualty Billing Process Using BaaS Provider
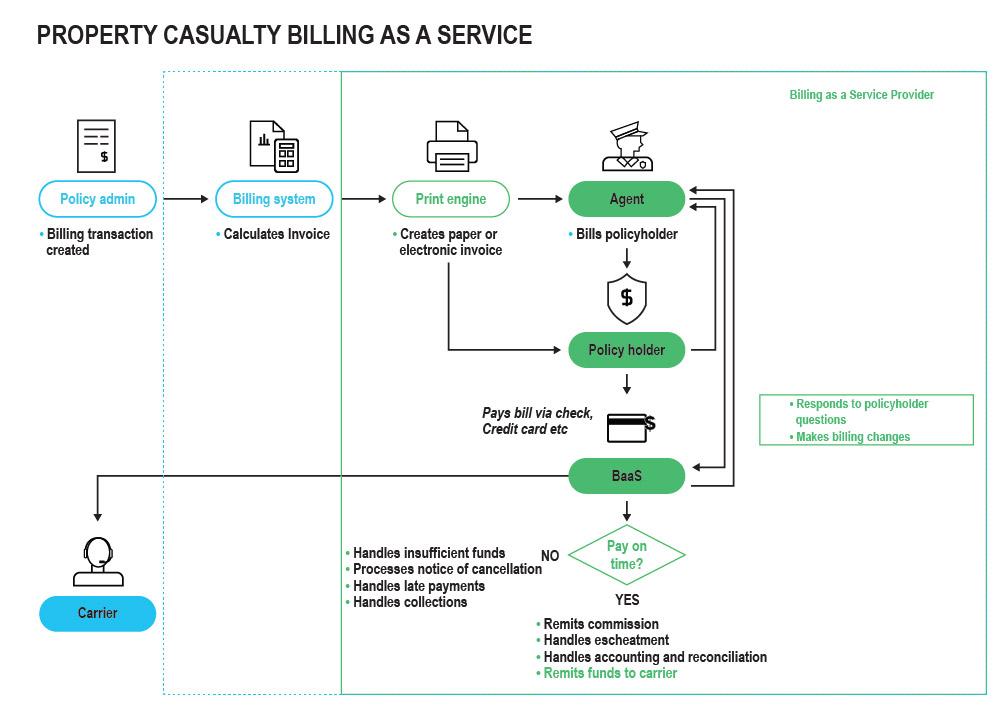
There are several variations of this model. Some, as described above, start by taking the feed from your billing system and handling all the tasks that follow. Some can take the feed from your policy admin system, essentially replacing the billing system. Some can simply pop a payment application onto your existing billing process, allowing the payor to use a mobile application — but having the insurer manage the rest of the billing process. Some offer premium finance capabilities as well.
Path Forward
BaaS is not the right solution for every insurer, but there are some who find this option to be of high value. It all comes down to a basic truth. Billing, while it can be technologically complex to implement properly, isn’t brain surgery. Rarely is it the component that makes an insurance company great. After all, every company can, one way or another, issue a bill and collect premium payments. But billing services do influence a customer’s perception of the insurer.
The flexibility of payment options, multiple payment mechanisms, and ease of self-service interaction with the insurer are becoming key expectations from customers influenced by their ability to interact with other noninsurance firms. Some insurers can deliver on these expectations easily. Others may find it easier to outsource billing in order to offer the experience customers are demanding.
Resources (both technological and administrative) allocated to billing take away from resources that should be dedicated to creating new products and servicing them. BaaS takes this non-strategic activity off the plate of the company so that the company can be creative and grow.
There is no single best BaaS provider for all insurers. There are a number of good choices for an insurer with almost any set of requirements. An insurer seeking a new BaaS provider should begin the process by looking inward. Every insurer has its own unique mix of lines of business, geography, staff capabilities, business objectives, and financial resources. This unique combination will influence the list of vendors for consideration.
We recommend that insurers looking for a BaaS provider narrow their choices by focusing on the following areas:
- Breadth and depth of transactional services provided.
- Level of customer service functions and relevant metrics to measure quality.
- Administrative support tools.
- The integration framework.
- The success of solution in similar business lines.
- The vendor's stability, knowledge, and investment in the solution.
- Customer reference interviews.
Insurers realize the strong role that billing, and especially the quality of service provided during the billing process, play in financial operations and in building relationships with customers and distributors. There is no question that BaaS presents a very viable and important option for insurance companies and MGAs.

REPORT
BILLING-AS-A-SERVICE (BaaS) FOR PROPERTY CASUALTY INSURERS
A PRIMER